
Privilege Escalation Techniques: Learn the art of exploiting Windows and Linux systems
InfoSec and Compliance – With 20 years of blogging experience, DISC InfoSec blog is dedicated to providing trusted insights and practical solutions for professionals and organizations navigating the evolving cybersecurity landscape. From cutting-edge threats to compliance strategies, this blog is your reliable resource for staying informed and secure. Dive into the content, connect with the community, and elevate your InfoSec expertise!
Mar 29 2022
Mar 29 2022
MalwareHunterTeam researchers discovered the malicious script on a compromised WordPress site, when the users were visiting the website the script launched a DDoS attack against ten Ukrainian sites.
The JavaScript was designed to perform thousands of HTTP GET requests to the targeted sites
The only evidence of the ongoing attack is the slowing down of the browser performance.
According to BleepingComputer, which first reported the discovery, DDoS attacks targeted pro-Ukrainian sites and Ukrainian government agencies, including think tanks, recruitment sites for the International Legion of Defense of Ukraine, and financial sites.
Below is the list targeted websites:
https://stop-russian-desinformation.near.page
https://gfsis.org/
http://93.79.82.132/
http://195.66.140.252/
https://kordon.io/
https://war.ukraine.ua/
https://www.fightforua.org/
https://bank.gov.ua/
https://liqpay.ua
https://edmo.euThe script generates random requests to avoid that they are served through a caching service.

BleepingComputer discovered that the same script is being used by the pro-Ukrainian site to launch attacks against Russian websites.
“When visiting the site, users’ browsers are used to conduct DDoS attacks on 67 Russian websites.” states BleepingComputer.
Mar 28 2022
Malicious schemas linked to online stores are on the rise in 2022. Criminal gangs from China have been using copies of online stores of popular brands to target users all over the world and thereby trick victims. The targets of this massive campaign are online stores geolocated in different countries, including Portugal, France, Spain, Italy, Chile, Mexico, Columbia, among others. The campaign has been active since late 2020 but gained momentum in early 2022, with thousands of victims affected.

Active domains behind the malicious online stores at the time of analysis (21-03-2022). The shopping platforms are available on servers geolocated in the USA, The Netherlands, and Turkey (ZoomEye).
As observed in Figure 1, 617 active shopping platforms were identified worldwide, 562 created in 2022. The servers are located in three countries: the USA, The Netherlands, and Turkey. However, other servers and online stores were also identified during the research. The complete list of IoCs with more than 1k malicious entries is provided at the end of the article.
The high-level diagram of this campaign is presented below, with a graphical representation of the different steps and actions carried out by criminals.
A new campaign typically starts with the authors setting up the malicious domain at the top of Google search through digital ads (Google ads) – as shown above referring to the Lefties clothing store disseminated in Portugal in 2022. After some days, users are hit as the malicious URL appears at the top of searches. In specific cases, social Ads were also found on Instagram and Facebook social media platforms.
The content of the malicious websites – clones of the official stores – are based on a static Content Management System (CMS) and a PHP API that communicates with a MySQL cluster in the background. Some artifacts related to the static CMS can be found on a GitHub repository from criminals. In detail, criminals put some effort into developing a generic platform that could serve a mega operation at a large scale, where small tweaks of images and templates would allow the reuse of code for different online stores. Then, all the observed stores use the same code with different templates according to the target brand. As mentioned, the store is also equipped with an API that communicates with a MySQL database cluster where all the victims’ data is stored, including:
As usual, this Personally Identifiable Information (PII) can be utilized later by criminals to leverage other kinds of campaigns. In order to prevent this type of scenario, we provide a tool that allows you to validate if victims’ information is now in the wrong hands.
Scam Me If You Can: Simple Strategies to Outsmart Today’s Rip-off Artists
Mar 26 2022
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) added multiple Kaspersky products and services to its Covered List saying that they pose unacceptable risks to U.S. national security.
“The Federal Communications Commission’s Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau today added equipment and services from three entities – AO Kaspersky Lab, China Telecom (Americas) Corp, and China Mobile International USA Inc. – to its list of communications equipment and services that have been deemed a threat to national security, consistent with requirements in the Secure and Trusted Communications Networks Act of 2019.” reads the FCC’s press release.
The Covered List, published by Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau published, included products and services that could pose an unacceptable risk to the national security of the United States or the security and safety of United States persons.
The US commission also added Chinese state-owned mobile service providers China Mobile International USA and China Telecom Americas to the list. Below is the list of Covered Equipment or Services added on March 25, 2022:
FCC banned Kaspersky security solutions and services supplied by Kaspersky or any linked companies.
“The FCC’s decision to add these three entities to our Covered List is welcome news. The FCC plays a critical role in securing our nation’s communications networks, and keeping our Covered List up to date is an important tool we have at our disposal to do just that. In particular, I am pleased that our national security agencies agreed with my assessment that China Mobile and China Telecom appeared to meet the threshold necessary to add these entities to our list. Their addition, as well as Kaspersky Labs, will help secure our networks from threats posed by Chinese and Russian state backed entities seeking to engage in espionage and otherwise harm America’s interests.” said FCC Commissioner Brendan Carr. “I applaud Chairwoman Rosenworcel for working closely with our partners in the Executive Branch on these updates. As we continue our work to secure America’s communications networks, I am confident that we will have more entities to add to our Covered List.”

In Mid March, the German Federal Office for Information Security agency, aka BSI, recommended consumers uninstall Kaspersky anti-virus software. The Agency warns the cybersecurity firm could be implicated in hacking attacks during the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine.
According to §7 BSI law, the BSI warns against the use of Kaspersky Antivirus and recommends replacing it asap with defense solutions from other vendors.
Mar 25 2022
Mar 25 2022
Google fixed an actively exploited high-severity zero-day vulnerability with the release of Chrome 99.0.4844.84 for Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Google has released Chrome 99.0.4844.84 for Windows, Mac, and Linux users to address a high-severity zero-day bug, tracked as CVE-2022-1096, exploited in the wild.
The CVE-2022-1096 vulnerability is a Type Confusion in V8 JavaScript engine, the bug was reported by an anonymous on 2022-03-23.
“The Stable channel has been updated to 99.0.4844.84 for Windows, Mac and Linux which will roll out over the coming days/weeks.” reads the security advisory published by Google.
“Google is aware that an exploit for CVE-2022-1096 exists in the wild.”
At this time, Google has yet to publish technical details about the flaw ether how it was exploited by threat actors in the wild.
“Access to bug details and links may be kept restricted until a majority of users are updated with a fix. We will also retain restrictions if the bug exists in a third party library that other projects similarly depend on, but haven’t yet fixed.” continues the advisory.
The CVE-2022-0609 zero-day is a use after free issue that resides in Animation, the bug was reported by Adam Weidemann and Clément Lecigne of Google’s Threat Analysis Group.
The flaw was exploited by North Korea-linked threat actors since January 4, 2022.
Mar 24 2022
The ongoing global turmoil has tested the supply chain across industries in a myriad of ways – from strained resources and remote workflows to security concerns and more. Sustaining a resilient supply chain is one area where many organizations have seen disruptions and business risk, mostly related to managing third-party vendors.
Recent reports have found that 85% of companies are losing money to third-party integration issues related to their supply chains – some losing over $1 million per year. Much of this is contributed by outdated integration systems – those that are not cloud-based – as well as a lack of end-to-end business process visibility. In addition, 35% of businesses have stated their compliance teams have no way of knowing if third-party partners are compliant. Not only is this a big problem financially, but it indicates that most aren’t aware of what is happening across business transactions, which could contribute to even greater future risk and loss.
To overcome these challenges, businesses must implement an agile risk management program that prioritizes third-party risk management. Building a formalized third-party risk management program that strengthens end-to-end process visibility is a three-step process.
Defining the current state of an IT and third-party risk management program is the first step in understanding what is working, and most critically, what is not working. This includes a complete audit of existing vendors and the potential risks they pose; this gives leaders visibility into current risks, identifies addressable risk, and unnecessary future risks that can be preemptively mitigated. This process also enables organizations to create new standards and goals for an improved third-party vendor program. For example, organizations need to understand communication processes between IT and third-party risk management teams to unearth potential issues caused by manual processes, inadequate reporting and/or inaccessibility to relevant data.
Top-down sponsorship and bottom-up execution is also key when developing a third-party compliance program. Organization-wide alignment shifts third-party vendor processes from a “check box” compliance exercise to a consistent, thorough process that underscores the significance of having a risk management program in place. For example, many organizations have a vendor onboarding checklist that includes tasks like reviewing their product/service track record, financial stability and if they’ve run afoul of the law. However, a consistent, thorough process would also encompass activities like ongoing due diligence that regularly checks a vendor’s risk profile for financial, regulatory, and reputational risk.
To break down silos and make adoption more seamless, organizations should consider automating these processes, and integrating with systems of record across the business. This will grow program efficacy, create greater efficiency in operations and most importantly, will support a risk management program that can evolve alongside future compliance needs, workflows, and processes.
A primary reason executive sponsorship is critical is because organizations need to determine what resources are available to actualize plans.
Key stakeholders across IT, HR and risk and compliance will be instrumental in not just the rollout of an improved third-party vendor program, but also in defining the scope. Allocating resources can be anything from identifying internal subject matter experts, formalizing committees, or determining if and how new hires need to be evaluated.
Because you can’t boil the ocean, it is important to understand which vendors have the greatest potential impact to the business. With this data in hand – which is accessed by foundational assets like robust risk management tools and solutions – project stakeholders can prioritize risks by level of importance and formulate an actionable plan.
Lastly, establishing and enforcing a library of controls within these solutions can improve processes and decrease the level of risk. By doing so, the organization can manage enforcement for internal as well as regulatorily enforced best practices, while also ensuring that any third parties with access to these systems follow the same requirements, thereby creating uniformity of process and reducing risk.
In addition to assessing third parties, a key step in building a healthy risk management program is defining metrics. The program methodology should include established reporting standards and target metrics, allowing success to be measured over time. With benchmarks from step one in place, teams can measure how cloud integrations led to overall improvements, or how quickly potential risks were rectified, for example.
Employee training plays a big role here as everyone within an organization needs to be able to navigate third-party risk management solutions with ease. Training should include the entire risk management function and provide repeatable introductions into the change management challenges that are associated with any new program, process, or system.
While a robust solution with automated workflows will certainly resolve integration issues and streamline processes, organizational buy-in for third-party risk management programs is what defines resilient vendor relationships and a healthy compliance program. Using this methodology to create a risk-based strategy will not only help a business establish and maintain a strong vendor supply chain but can help identify future risks enabling teams to mitigate them before they become a business-impacting issue, which is what businesses resilience is all about.

Cybersecurity and Third-Party Risk: Third Party Threat Hunting
Mar 24 2022
Mar 24 2022
In late 2021, Volexity researchers investigated an intrusion in an environment they were monitoring and discovered a MacBook Pro running macOS 11.6 (Big Sur) that was compromised with a previously unknown macOS malware tracked as GIMMICK. The researchers explained that they have discovered Windows versions of the same implant during the past investigations.
The experts attribute the intrusion to a China-linked APT group tracked as Storm Cloud, which is known to target organizations across Asia.
The macOS version of the implant is written primarily in Objective C, while the Windows ones are in both .NET and Delphi. The implant uses public cloud hosting services (such as Google Drive) for C2 to evade detection.
Volexity worked with Apple to implement protections for the GIMMICK implant, on March 17, 2022, Apple pushed new signatures to XProtect and MRT to remove the malware.

GIMMICK should be launched directly by a user, rather than a daemon, then it installs itself as a launch agent by dropping a PLIST file with contents.
“On macOS, GIMMICK was found to support being launched as a daemon on the system or by a user. Should GIMMICK be launched directly by a user, rather than a daemon, it will install itself as a launch agent by dropping a PLIST file with contents, similar to that shown below, to /Users/<username>/Library/LaunchAgents.” reads the analysis published by Volexity. “The name of the binary, PLIST, and agent will vary per sample. In the case observed by Volexity, the implant was customized to imitate an application commonly launched by the targeted user.”
During the initialization, the implant analyzed by the experts decodes several pieces of data used by the implant for its operation using a rotating addition algorithm.
The implant also supports an uninstall function accessible by adding the argument “uninstall” on the command line. The command instructs the malicious code on removing itself and all associated files, and then kills the process.
“Storm Cloud is an advanced and versatile threat actor, adapting its tool set to match different operating systems used by its targets.” concludes the analysis published by the experts. “The work involved in porting this malware and adapting its systems to a new operating system (macOS) is no light undertaking and suggests the threat actor behind it is well resourced, adept, and versatile.”
Attribution of Advanced Persistent Threats: How to Identify the Actors Behind Cyber-Espionage
Mar 23 2022
“Most of America’s critical infrastructure is owned and operated by the private sector and critical infrastructure owners and operators must accelerate efforts to lock their digital doors,” he noted, and advised those that have not yet done it to harden their cyber defenses by implementing security best practices delineated earlier this year.
“[This warning is] based on evolving intelligence that the Russian Government is exploring options for potential cyberattacks,” he added.
US Deputy National Security Advisor Anne Neuberger has followed up the warning with a press briefing, during which she stated that “there is no certainty there will be a cyber incident on critical infrastructure,” but that owners and operators of critical infrastructre have the ability and the responsibility to harden the systems and networks the country relies on.
She shared that last week, federal agencies hosted classified briefings with several hundred companies in sectors they felt would be most affected, and “provided very practical, focused advice.”
Previously, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) released guidance to help critical infrastructure owners and operators identify and mitigate the risks of influence operations that use mis-, dis-, and malinformation (MDM) narratives.
Neuberger also said that US agencies have not yet attributed the recent attack on satellite communications company Viasat. Nevertheless, the attack has been followed by a CISA alert advising SATCOM network providers or customers on how to upgrade their defenses.

Mar 23 2022
Rafeeq Rehman CISO MindMap 2021: What do InfoSec professionals really do?
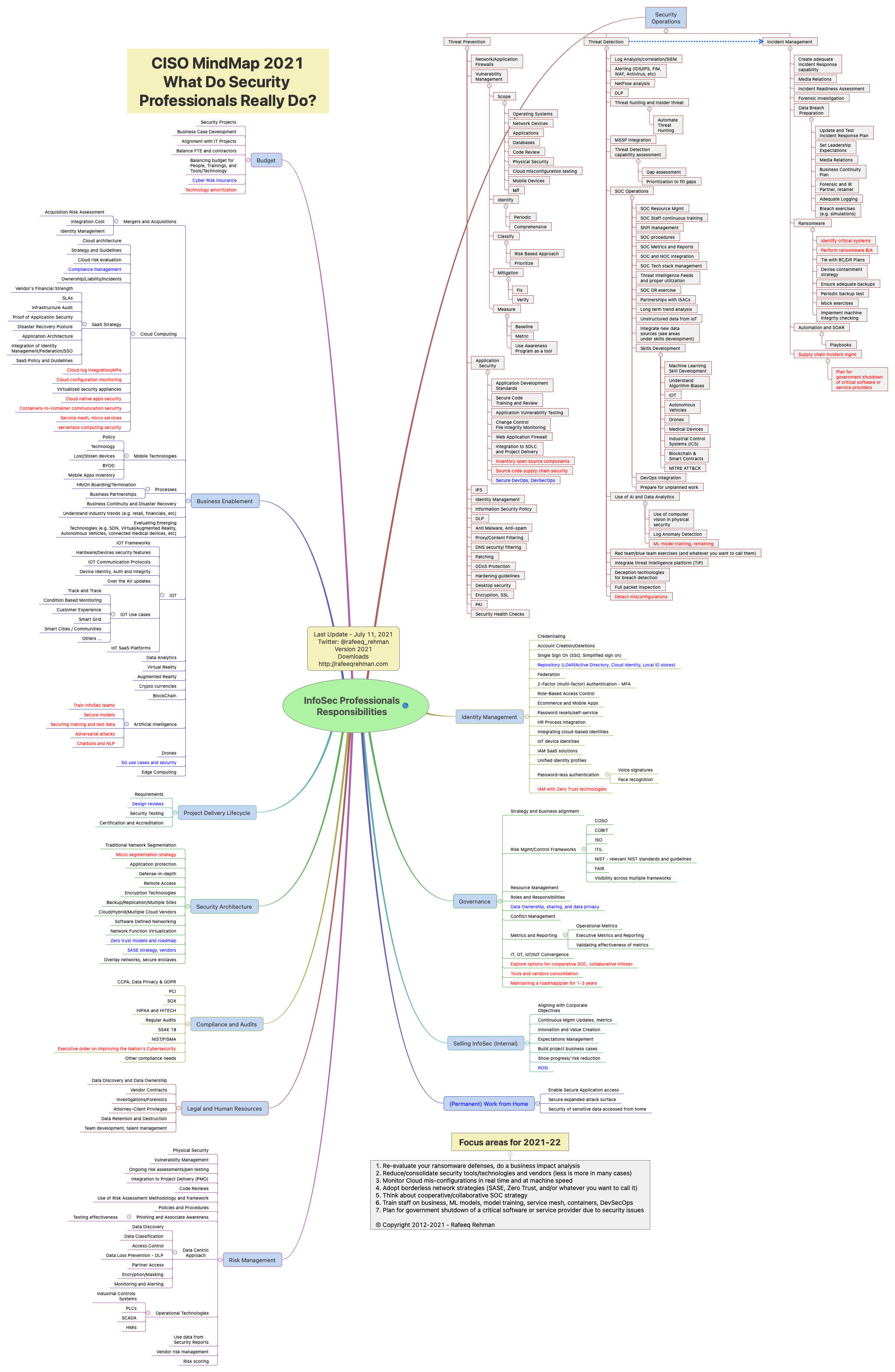
The CISO Evolution: Business Knowledge for Cybersecurity Executives
Mar 22 2022
You might have heard that the iPhone is almost completely impossible to hack or that Samsung devices have some of the best firewalls in the world built right into the device. While these statements are true, they do not mean that your personal information is automatically safe.
In fact, there are a handful of ways hackers can get into your mobile device. That being said, there are several steps you can take to fight back against it. So, let’s take a look and explore those in a bit more depth today.
Table of Contents

Wireless and Mobile Device Security
Mar 22 2022
The gang announced the alleged hack through its Telegram channel and shared a series of screenshots as proof of the hack. Some of the images published by the threat actors appear to be related to the company’s customer data.
The message published by the group claims that the gang had Superuser and Admin access to multiple systems of the company.

The company is investigating claims of a data breach which, if confirmed, could pose serious risks to the customers of the company.
“Okta is aware of the reports and is currently investigating,” states a spokesperson for the company. “We will provide updates as more information becomes available.”
Todd McKinnon, CEO at Okta, confirmed that in late January 2022, the company detected an attempt to compromise the account of a third party customer support engineer working for one of its subprocessors.
McKinnon added that there is no evidence of ongoing malicious activity that resulted from the activity detected in January.
Mar 21 2022
By now, we are all familiar with the fact that Log4Shell is just about as critical as a critical vulnerability can get – scoring a 10 out of 10 on the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s CVSS severity scale.
As it targets a library – Apache Log4j2 – that nearly every Java application uses to log requests, this vulnerability is ubiquitous. Many applications use Log4j2 without even realizing it, meaning that even those with no apparent dependency on Log4j2 can still be at risk.
With its massive impact across nearly every industry, Log4Shell has taken its place in the cybersecurity hall of fame – among the likes of HeartBleed, WannaCry and ShellShock.
Difficult to locate but easy to exploit, remediating this vulnerability would prove incredibly complex, with several detection methods required. In fact, three months into Log4Shell, the Qualys Cloud Platform suggests that 30% of the Log4j instances still remain unpatched.
When it came to tracking the impact of Log4Shell, Qualys occupies a unique vantage point. The Qualys Cloud Platform indexes more than 10 trillion data points across its installed enterprise customer base and completed 6 billion IP scans per year with 75 million cloud agents deployed in hybrid IT environments globally. With that kind of scale, the Qualys Research Team was able to uncover unique insights into how global enterprises have and are managing Log4Shell:
Log4j has been and will continue to be a headache for security professionals due to how difficult it is to fully understand where this vulnerability may be within an organization.
As with most vulnerabilities, understanding how and where the flaw will affect your business is crucial. Discovery processes are unique to each organization – meaning that depending on architecture and deployment, timetables vary.
This paired with obstacles such as the complexities of skeleton IT staff, potential lack of visibility into IT assets and an overall influx of other real-time sophisticated attacks and threats, could present a tumultuous road to immediate remediation.
The main culprit for why vulnerable versions continue to be downloaded is likely because of automated build systems. These are configured to download a specific version build of their dependencies. Lesser maintained projects may automatically download a specific version to avoid conflicts with updated software, which has the potential to break their code. If the maintainer of that software hasn’t been paying attention to Log4j news their application is left open to the risk of exploitation.
Another scenario is the intentional download by researchers or adversaries to test exploitation of their latest wares. It is useful for both good and bad guys to continually validate that their exploitations or defenses are in working order outside of production areas.
Flawed forms of the code are still available because many other pieces of software still rely on them. Removing these downloads could potentially cause breakage in several systems if eliminated.
Further, The Qualys Research team found that more than 50% of application installations with Log4j were flagged as “end of support.” These publishers will likely not be providing Log4Shell security patches for these apps. End of life/support technology is one of the leading factors that put organizations at risk of being exploited by threat actors.
In fact, earlier this year, CISA developed a catalog of “Bad Practices” to showcase what is exceptionally risky. Landing at number one – especially for organizations supporting Critical Infrastructure or NCFs – was the use of unsupported software.

Mar 21 2022
Hacker leaked a new version of the Conti ransomware source code on Twitter as retaliation of the gang’s support to Russia
The attack against the Conti ransomware and the data leak is retaliation for its support for the Russian invasion of Ukraine.

The attack will have a significant impact on the operation of the gang, considering also that many of Conti’s affiliates are Ukrainian groups.
Recently a Ukrainian researcher leaked 60,694 messages internal chat messages belonging to the Conti ransomware operation after the announcement of the group of its support to Russia. He was able to access the database XMPP chat server of the Conti group.
In a second round, the expert leaked the old source code for the Conti ransomware encryptor, decryptor, and builder, along with the administrative panel and the BazarBackdoor API. The leaked old Conti ransomware source code is dated September 15th, 2020.
The source code for the ransomware is contained in a password-protected archive, despite the researcher did not leak the password, another expert cracked it and share it.
The public availability of the source code could temporarily destroy the Conti ransomware operation because security experts could perform reverse engineering to determine how it works and develop a working decrypted.
On the other side, other threat actors could perform reverse engineering to develop their own version of the threat, a circumstance that opens to worrisome scenarios.
Now the Ukrainian security researcher has leaked newer malware source code from the Conti ransomware operation, the code is dated January 25th, 2021.
The code appears to be more recent than the previous leak, according to Bleeping Computer Conti Leaks uploaded the source code for Conti version 3 to VirusTotal and shared a link on Twitter.
“The source code compiles without error and can be easily modified by other threat actors to use their own public keys or add new functionality.” reported BleepingComputer. “BleepingComputer compiled the source code without any issues, creating the cryptor.exe, cryptor_dll.dll, and decryptor.exe executables.”
Ransomware Protection Playbook
Mar 17 2022
The Great Resignation is sweeping the world, and the causes and impacts are still being analyzed. Texas A&M University professor Anthony Klotz coined the term, predicting an unusual rise in voluntary resignations as employees anticipated the global pandemic coming to end and life returning to normal. Many employees stayed longer in roles because they were uncertain of the future during the pandemic, while frontline workers experienced an elevated level of burnout due to increased stress. Workers in all industries are looking for new opportunities and leaving past roles behind.
IT and security staff are resigning too, feeling increased stress from managing more remote employees, a rapid transition to the cloud that didn’t allow time for them to gain cloud expertise before making the leap, and a rise in cyberattacks globally. Finding and retaining security talent is an ongoing challenge, one that exposes organizations to increased risk because there simply aren’t enough security experts available.
Most employees, certainly in technology companies but in other industries as well, are required to undergo security training and sign non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) when they join a company. That’s frequently the last time they consider security training, how they use personal devices for company communications and data, and what data belongs to the company and what data they’re permitted to share externally or take with them when they leave. Much of this information is only communicated in an NDA, a document that’s rarely read carefully or reviewed regularly. This may result in reduced adherence to security rules and practices — and, consequently, data losses. Some disgruntled employees may even be tempted to disclose sensitive information or leave security holes to allow them to access the company’s IT infrastructure after departure.
All employees have access to secrets, whether that’s a product strategy document, internal lists of sales prospects or customers, or other internal communications or presentations that aren’t intended for external consumption. Security and engineering teams have access to many internal systems, passwords, and secrets. When many employees leave an organization in a brief period, risks increase because there are so many things to take care of for so many people at the same time.

Off-boarding employees can pose challenges for any organization. In the past year, data exfiltration incidents increased due to employees taking data, systems access, or both with them when they exit. This is when organizations can refer to their onboarding plan to create a successful off-boarding plan, one that includes people, process, and technology.
Rather than taking a reactive approach to employees leaving the company, embrace a readiness-mindset and prepare for departures in advance. To do that, here are essential steps to take so that you’re ready for employee departures:
Successfully off-boarding security staff introduces some added considerations. While the preceding steps are still critical, security staff have increased access and knowledge when it comes to your systems and infrastructure. Once again, people, process, and technology all play a role. Monitor and audit access to sensitive corporate data, particularly noting whether they’re being accessed by computers or IP addresses outside of the corporate network. Former employees also still have relationships with current staff, so flag and investigate unusual activity there as well.
Adopting a zero-trust framework will help you protect resources even when critical security staff members leave the organization. Putting clear and easily repeatable processes in place can also help you reduce security risks due to departing staff, such as turning off email access but automatically forwarding all email and voicemail to a supervisor so that nothing gets missed. Your process should also include rolling any secrets they have access to promptly, rotating access, and removing their accounts from every system.
Cybersecurity Career Master Plan
Mar 17 2022
Researchers from Qihoo 360’s Netlab have discovered a new backdoor used to infect Linux systems and include them in a botnet tracked as B1txor20.
The malware was first spotted on February 9, 2022, when 360Netlab’s honeypot system captured an unknown ELF file that was spreading by exploiting the Log4J vulnerability.
The name B1txor20 is based on the file name “b1t” used for the propagation and the XOR encryption algorithm, and the RC4 algorithm key length of 20 bytes.
The B1txor20 Linux backdoor uses DNS Tunnel technology for C2 communications, below is the list of the main features implemented by the threat:

The researchers also noticed the presence of many developed features that have yet to be used, and some of them are affected by bugs. Experts believe the B1txor20 botnet is under development.
“In short, B1txor20 is a Backdoor for the Linux platform, which uses DNS Tunnel technology to build C2 communication channels. In addition to the traditional backdoor functions, B1txor20 also has functions such as opening Socket5 proxy and remotely downloading and installing Rootkit.” reads the analysis published by the experts.
Once the system has been compromised, the threat connects the C2 using the DNS tunnel and retrieves and executes commands sent by the server. The researchers noticed that the bot supports a total of 14 commands that allows it to execute arbitrary commands, upload system information, manipulate files, starting and stopping proxy services, and creating reverse shells.
“Generally speaking, the scenario of malware using DNS Tunnel is as follows: Bot sends the stolen sensitive information, command execution results, and any other information that needs to be delivered, after hiding it using specific encoding techniques, to C2 as a DNS request; After receiving the request, C2 sends the payload to the Bot side as a response to the DNS request. In this way, Bot and C2 achieve communication with the help of DNS protocol.” continues the analysis.
The post includes additional technical details along with Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) for this threat.
Indicators of Compromise Associated with BlackByte Ransomware: Joint Cybersecurity Advisory
Mar 16 2022
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added 15 vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog.
According to Binding Operational Directive (BOD) 22-01: Reducing the Significant Risk of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities, FCEB agencies have to address the identified vulnerabilities by the due date to protect their networks against attacks exploiting the flaws in the catalog.
Experts recommend also private organizations review the Catalog and address the vulnerabilities in their infrastructure.
The new vulnerabilities added to the catalog include one SonicWall SonicOS issue, tracked as CVE-2020-5135, and 14 Microsoft Windows flaws addressed between 2016 and 2019.
The CVE-2020-5135 is a stack-based buffer overflow that affects the SonicWall Network Security Appliance (NSA). The vulnerability can be exploited by an unauthenticated HTTP request involving a custom protocol handler.
The flaw resides in the HTTP/HTTPS service used for product management as well as SSL VPN remote access.
All the flaws added in this round have to be addressed by federal agencies by April 5.
The CISA Catalog has reached a total of 504 entries with the latest added issues.

Mar 15 2022

President Joe Biden on Tuesday signed into law a $1.5 million government funding bill that includes legislation mandating critical infrastructure owners report if their organization has been hacked or made a ransomware payment.
Biden signed the legislation during a White House ceremony that was attended by administration officials and top Democratic lawmakers, including including House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (Calif.), Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (N.Y.).
The Strengthening American Cybersecurity Act — which was attached to the spending deal that keeps the federal government open until September — requires that critical infrastructure operators alert the Homeland Security Department’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) within 72 hours of a breach and 24 hours if the organization made a ransomware payment. It also grants CISA the power to subpoena entities that don’t report a cyber incident or ransomware payment.
The measure becoming law is a complete reversal from only a few months ago when it was stripped from the annual defense policy bill.
CISA will have up to two years to publish a notice in the Federal Register on proposed rulemaking to implement the reporting effort, though it may move faster due to heightened concerns about Russian cyberattacks bleeding out of Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine.
“This historic, new law will make major updates to our cybersecurity policy to ensure that, for the first time ever, every single critical infrastructure owner and operator in America is reporting cyber-attacks and ransomware payments to the federal government,” Senate Homeland Security Committee Chair Gary Peters (D-Mich.), who authored and championed the legislation along with Sen. Rob Portman (R-Ohio), said in a statement.
Portman, the panel’s top Republican said the legislation will “give the National Cyber Director, CISA, and other appropriate agencies broad visibility into the cyberattacks taking place across our nation on a daily basis to enable a whole-of-government response, mitigation, and warning to critical infrastructure and others of ongoing and imminent attacks.”
https://
