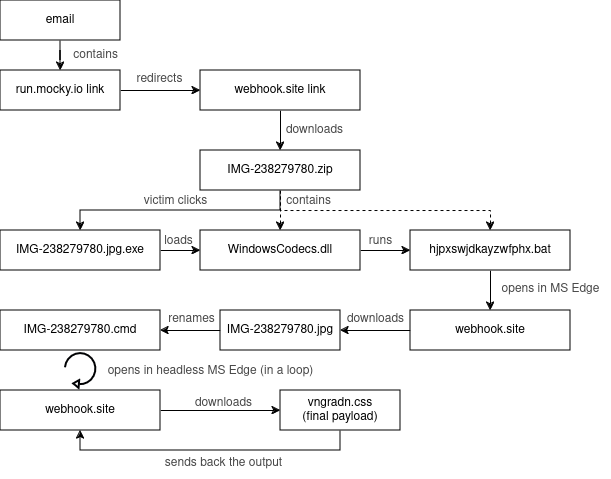
A significant security vulnerability has been discovered by Tenable Research that affects Azure customers relying on Service Tags for their firewall rules. This vulnerability allows attackers to bypass Azure firewall rules, posing a substantial risk to organizations using these configurations. Here’s an in-depth look at the vulnerability, how it can be exploited, and crucial defensive measures to mitigate the risk.
INITIAL DISCOVERY IN AZURE APPLICATION INSIGHTS
Tenable Research initially uncovered the vulnerability within Azure Application Insights, a service designed to monitor and analyze web applications’ performance and availability. The Availability Tests feature of Azure Application Insights, intended to check the accessibility and performance of applications, was found to be susceptible to abuse. Users can control server-side requests in these tests, including adding custom headers and changing HTTP methods. This control can be exploited by attackers to forge requests from trusted services, mimicking a server-side request forgery (SSRF) attack.

EXPANSION TO MORE THAN 10 OTHER AZURE SERVICES
Upon further investigation, Tenable Research found that the vulnerability extends beyond Azure Application Insights to more than 10 other Azure services. These include:
- Azure DevOps
- Azure Machine Learning
- Azure Logic Apps
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Load Testing
- Azure API Management
- Azure Data Factory
- Azure Action Group
- Azure AI Video Indexer
- Azure Chaos Studio
Each of these services allows users to control server-side requests and has an associated Service Tag, creating potential security risks if not properly mitigated.
HOW ATTACKERS CAN EXPLOIT THE VULNERABILITY
Attackers can exploit the vulnerability in Azure Service Tags by abusing the Availability Tests feature in Azure Application Insights. Below are detailed steps and examples to illustrate how an attacker can exploit this vulnerability:
1. Setting Up the Availability Test:
- Example Scenario: An attacker identifies an internal web service within a victim’s Azure environment that is protected by a firewall rule allowing traffic only from Azure Application Insights.
- Action: The attacker sets up an Availability Test in Azure Application Insights, configuring it to target the internal web service.
2. Customizing the Request:
- Manipulating Headers: The attacker customizes the HTTP request headers to include authorization tokens or other headers that may be expected by the target service.
- Changing HTTP Methods: The attacker can change the HTTP method (e.g., from GET to POST) to perform actions such as submitting data or invoking actions on the target service.
- Example Customization: The attacker configures the test to send a POST request with a custom header “Authorization: Bearer <malicious-token>”.
3. Sending the Malicious Request:
- Firewall Bypass: The crafted request is sent through the Availability Test. Since it originates from a trusted Azure service (Application Insights), it bypasses the firewall rules based on Service Tags.
- Example Attack: The Availability Test sends the POST request with the custom header to the internal web service, which processes the request as if it were from a legitimate source.
4. Accessing Internal Resources:
- Unauthorized Access: The attacker now has access to internal APIs, databases, or other services that were protected by the firewall.
- Exfiltration and Manipulation: The attacker can exfiltrate sensitive data, manipulate internal resources, or use the access to launch further attacks.
- Example Impact: The attacker retrieves confidential data from an internal API or modifies configuration settings in an internal service.
DETAILED EXAMPLE OF EXPLOIT
Scenario: An organization uses Azure Application Insights to monitor an internal financial service. The service is protected by a firewall rule that allows access only from the ApplicationInsightsAvailability Service Tag.
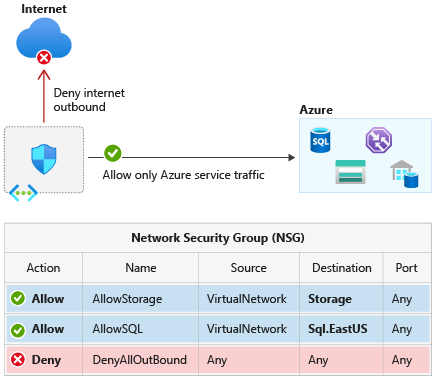
- Deploying an Internal Azure App Service:
- The organization has a financial application hosted on an Azure App Service with firewall rules configured to accept traffic only from the ApplicationInsightsAvailability Service Tag.
- Attempted Access by the Attacker:
- The attacker discovers the endpoint of the internal financial application and attempts to access it directly. The firewall blocks this attempt, returning a forbidden response.
- Exploiting the Vulnerability:
- Setting Up the Test: The attacker sets up an Availability Test in Azure Application Insights targeting the internal financial application.
- Customizing the Request: The attacker customizes the test to send a POST request with a payload that triggers a financial transaction, adding a custom header “Authorization: Bearer <malicious-token>”.
- Sending the Request: The Availability Test sends the POST request to the internal financial application, bypassing the firewall.
- Gaining Unauthorized Access:
- The financial application processes the POST request, believing it to be from a legitimate source. The attacker successfully triggers the financial transaction.
- Exfiltration: The attacker sets up another Availability Test to send GET requests with custom headers to extract financial records from the application.
ADVANCED EXPLOITATION TECHNIQUES
1. Chain Attacks:
- Attackers can chain multiple vulnerabilities or services together to escalate their privileges and impact. For example, using the initial access gained from the Availability Test to find other internal services or to escalate privileges within the Azure environment.
2. Lateral Movement:
- Once inside the network, attackers can move laterally to compromise other services or extract further data. They might use other Azure services like Azure DevOps or Azure Logic Apps to find additional entry points or sensitive data.
3. Persistent Access:
- Attackers can set up long-term Availability Tests that periodically execute, ensuring continuous access to the internal services. They might use these persistent tests to maintain a foothold within the environment, continuously exfiltrating data or executing malicious activities.
DEFENSIVE MEASURES
To mitigate the risks associated with this vulnerability, Azure customers should implement several defensive measures:
1. Analyze and Update Network Rules:
- Conduct a thorough review of network security rules.
- Identify and analyze any use of Service Tags in firewall rules.
- Assume services protected only by Service Tags may be vulnerable.
2. Implement Strong Authentication and Authorization:
- Add robust authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Use Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for managing access.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication and least privilege principles.
3. Enhance Network Isolation:
- Use network security groups (NSGs) and application security groups (ASGs) for granular isolation.
- Deploy Azure Private Link to keep traffic within the Azure network.
4. Monitor and Audit Network Traffic:
- Enable logging and monitoring of network traffic.
- Use Azure Monitor and Azure Security Center to set up alerts for unusual activities.
- Regularly review logs and audit trails.
5. Regularly Update and Patch Services:
- Keep all Azure services and applications up to date with security patches.
- Monitor security advisories from Microsoft and other sources.
- Apply updates promptly to minimize risk.
6. Use Azure Policy to Enforce Security Configurations:
- Deploy Azure Policy to enforce security best practices.
- Create policies that require strong authentication and proper network configurations.
- Use Azure Policy initiatives for consistent application across resources.
7. Conduct Security Assessments and Penetration Testing:
- Perform regular security assessments and penetration testing.
- Engage with security experts or third-party services for thorough reviews.
- Use tools like Azure Security Benchmark and Azure Defender.
8. Educate and Train Staff:
- Provide training on risks and best practices related to Azure Service Tags and network security.
- Ensure staff understand the importance of multi-layered security.
- Equip teams to implement and manage security measures effectively.
The vulnerability discovered by Tenable Research highlights significant risks associated with relying solely on Azure Service Tags for firewall rules. By understanding the nature of the vulnerability and implementing the recommended defensive measures, Azure customers can better protect their environments and mitigate potential threats. Regular reviews, updates, and a multi-layered security approach are essential to maintaining a secure Azure environment.
InfoSec services | InfoSec books | Follow our blog | DISC llc is listed on The vCISO Directory | ISO 27k Chat bot


















.webp)