
Blockchain: Understanding Its Uses and Implications
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services

Apr 16 2023
Apr 09 2023
Apr 09 2023
Apr 08 2023

Abu Dhabi and Dubai have have been ranked as the smartest cities in the Middle East and North Africa region.in the ‘Smart City Index 2021’. The index, by the Institute for Management Development (IMD), in collaboration with Singapore University for Technology and Design (SUTD) surveys residents in ranked cities to assess smart infrastructure and services covering health and safety, mobility, activities, opportunities, and governance.
According to ITU, a smart sustainable city is an innovative city that uses information and communication technologies (ICTs) and other means to improve quality of life, efficiency of urban operation and services, and competitiveness, while ensuring that it meets the needs of present and future generations with respect to economic, social and environmental aspects.
In 2016, the ITU, the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) and the UN Habitat launched the initiative ‘United for Smart Sustainable Cities’ (U4SSC). The U4SSC developed a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) for Smart Sustainable Cities (SSC) to establish the criteria to evaluate the contribution of ICT in making cities smarter and more sustainable, and to provide cities with the means for self-assessments in order to achieve the sustainable development goals (SDGs).
The State of Play of Sustainable Cities and Buildings in the Arab Region-2017
The State of Play of Sustainable Cities and Buildings in the Arab Region Report (PDF 26.19 MB) is a compilation of the main public policies, programmes, case studies, organisations and initiatives associated with sustainable city and building practices in twelve countries in the Arab region. Read about the UAE’s current situation with respect to sustainable cities from pages 79 to 86.
Read more on:
The UAE Government aims to ensure sustainable development while preserving the environment and to achieve a perfect balance between economic and social development. Abu Dhabi and Dubai are planning and developing several smart sustainable cities.
For the second year in a row, Abu Dhabi and Dubai have been ranked as the smartest cities in the Middle East and North Africa region, as per the Smart City Index 2021.
While Abu Dhabi is ranked 28, Dubai is closely behind at 29, out of 118 cities. Compared to 2020, both the emirates climbed up 14 places globally.
The top three smart cities are:

Explore how New Zealand is using technology and data to design sustainable smart cities.
Smart Cities: MIT Press Essential Knowledge Series – audio book $0.00
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services

Apr 06 2023

The malware is designed to monitor browser activity, take screenshots, and steal cryptocurrency through scripts injected in web pages.
Researchers at Trustwave SpiderLabs found that Rilide mimicked benign Google Drive extensions to hide in plain sight while abusing built-in Chrome functionalities.
The cybersecurity company detected two separate campaigns that distributed Rilide. One was using Google Ads and Aurora Stealer to load the extension using a Rust loader. The other one distributed the malicious extension using the Ekipa remote access trojan (RAT).
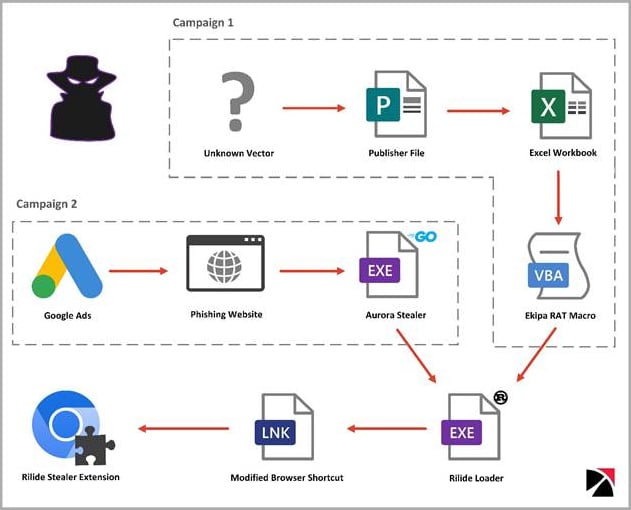
While the origin of the malware is unknown, Trustwave reports that it has overlaps with similar extensions sold to cybercriminals. At the same time, portions of its code were recently leaked on an underground forum due to a dispute between cybercriminals over unresolved payment.
Rilide’s loader modifies the web browser shortcut files to automate the execution of the malicious extension that is dropped on the compromised system.
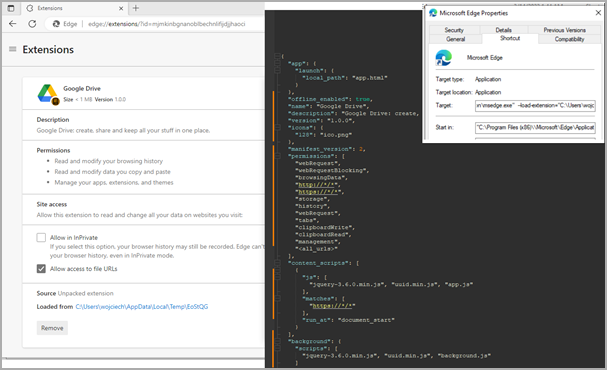
If there’s a match, the extension loads additional scripts injected into the webpage to steal from the victim information related to cryptocurrencies, email account credentials, etc.
The extension also disables ‘Content Security Policy,’ a security feature designed to protect against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, to freely load external resources that the browser would normally block.
In addition to the above, the extension regularly exfiltrates browsing history and can also capture screenshots and send them to the C2.
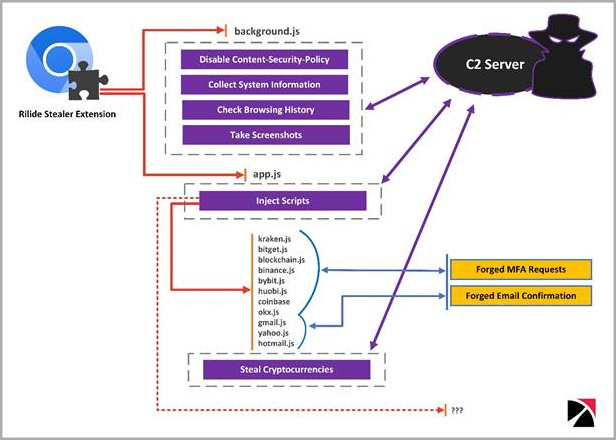
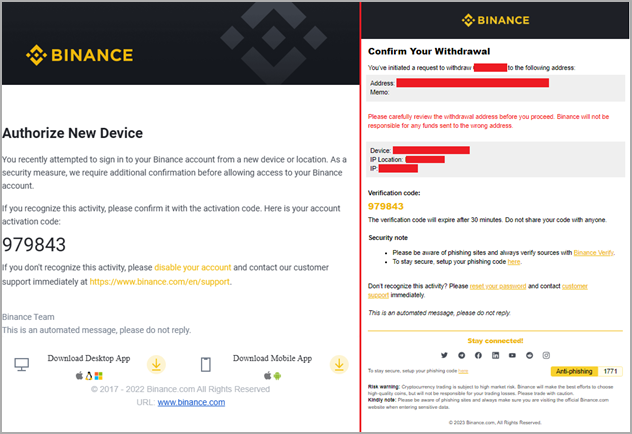
An interesting feature in Rilide is its 2FA-bypassing system, which uses forged dialogs to deceive victims into entering their temporary codes.
The system is activated when the victim initiates a cryptocurrency withdrawal request to an exchange service that Rilide targets. The malware jumps in at the right moment to inject the script in the background and process the request automatically.
Once the user enters their code on the fake dialog, Rilide uses it to complete the withdrawal process to the threat actor’s wallet address.
“Email confirmations are also replaced on the fly if the user enters the mailbox using the same web browser,” explains Turstwave in the report.
“The withdrawal request email is replaced with a device authorization request tricking the user into providing the authorization code.”
Rilide showcases the growing sophistication of malicious browser extensions that now come with live monitoring and automated money-stealing systems.
While the roll-out of Manifest v3 on all Chromium-based browsers will improve resistance against malicious extensions, Trustwave comments that it won’t eliminate the problem.
source:
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services

Mar 30 2023
Mar 30 2023
Mar 27 2023

In response to a recent vulnerability identified in Outlook, Microsoft recently published a proper guide for its customers to help them discover the associated IoCs.
That Outlook vulnerability in question has been tracked as “CVE-2023-23397” with a CVSS score of 9.8 and marked as Critical.
As a result of this flaw, NTLM hashes can be stolen, and without any user interaction, they can be reused to execute a relay attack.
The threat actors use specially crafted malicious emails to exploit the vulnerability and manipulate the victim’s connection. As a result, this allows them to get control of an untrusted location.

The attacker can authenticate as the victim with the Net-NTLMv2 hash leaked to the untrusted network.
In the Patch Tuesday updates for March 2023, Microsoft fixed the vulnerability in order to prevent the possibility of any further attacks.
The problem is that this approach was taken after it was weaponized by Russian threat actors and used as a weapon against the following sectors in Europe:
It was reported in April 2022 that Microsoft’s incident response team had found evidence that the shortcoming could be exploited.
It has been identified that a Net-NTLMv2 Relay attack allowed a threat actor to gain unauthorized entry to an Exchange Server in one attack chain.

By exploiting this vulnerability, the attacker could modify mailbox folder permissions and maintain persistent access, posing a significant security risk.
The adversary used the compromised email account in the compromised environment to extend their access. It has been discovered that this is done by sending additional malicious messages through the same organization to other members.
CVE-2023-23397 can lead to credential compromise in organizations if they do not implement a comprehensive threat-hunting strategy.
As a first step, running the Exchange scanning script provided by Microsoft is important to detect any malicious activity. However, it’s imperative to note that for all scenarios, this script is not capable of providing any visibility into messages that are malicious in nature.
Multiple mailboxes can be opened at the same time by Outlook users. Messages received through one of the other services will still trigger the vulnerability if a user configured Outlook to open mailboxes from multiple services. The scanned mailboxes do not contain that message.
If a user wishes to move a message to a local file, they can do so. Finding evidence of a prior compromise in Archived messages may be possible in some cases.
You can no longer access your Exchange messages if they have been deleted from Exchange. It is recommended that incident responders review the security telemetry collected from all available channels in order to confirm the presence of IP addresses and URIs obtained from the PidLidReminderFileParameter values.
There are a number of data sources that can be used to gather data, including:-
Here below we have mentioned all the recommendations:-
Source:
Mar 24 2023
It is the third day of the PWN2OWN VANCOUVER 2023 hacking contest. So far, security researchers managed to crack the operating systems Ubuntu, macOS and Windows 11, and other products, including Tesla cars and Adobe Reader.
Security researchers who managed to hack their targets win price money and the hacked devices, even if it is a Tesla.
Six of the eight hacks on day one were successful, a seventh was also successful, but it used an exploit that was known previously. Only one attempt failed to hack the target in time.

Here is the day one overview:
A total price money of $375,000 was awarded to the successful researchers and teams. The Tesla Model 3 changed owner as well.
On day two, security researchers managed to hack Oracle VirtualBox, Microsoft Teams, another Tesla, and Ubuntu Desktop.
Here is the day two overview:
The researchers received $475,000 in price money on the second day.
Attacks against Ubuntu Desktop, Microsoft Teams, Microsoft Windows 11, and VMWare Workstation are planned for the third and final day of the hacking competition.
Additional information about the successful hacks and exploits have not been released to the public. Companies whose products have been exploited will create security patches to protect their devices and applications from potential attacks targeting the bugs.
Expect security updates for all hacked products in the coming days and weeks.
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services
Mar 13 2023
Vendor Security Checklist – by Ministry of Security

Third Party Risk Management

Previous posts on Vendor Assessment
DISC performs Vendor assessment, we’d love to hear from you! If you have any questions, comments, or feedback, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team is here to help and we’re always looking for ways to improve our services. You can reach us by email (info@deurainfosec.com), or through our website’s contact form
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services
Mar 10 2023
The threat actor who posted the data for sale has claimed credit for multiple other breaches, including one at grocery platform Weee! that exposed data on more than 1.1 million customers.
Jai VijayanContributing Writer, Dark Reading

Hundreds of US lawmakers and their families are at risk of identity theft, financial scams, and potentially even physical threats after a known info-theft threat actor called IntelBroker made House of Representatives members’ personally identifiable information (PII) available for sale on the “Breached” criminal forum.
The information, confirmed as being obtained via a breach at health insurance marketplace DC Health Link, includes names, Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, and other sensitive identifying information. The data on the House members was part of a larger data set of PII belonging to more than 170,000 individuals enrolled with DC Health Link that the threat actor put up for sale this week.
In a March 8 email to members of the House and their staff, US House Chief Administrative Officer Catherine Szpindor said the attack on DC Health Link does not appear to have specifically targeted US lawmakers. But the breach was significant and potentially exposed PII on thousands of people enrolled with DC Health Link.
“The FBI also informed us that they were able to purchase this PII, along with other enrollee information, on the Dark Web,” Speaker of the House Kevin McCarthy (R-Calif.) and House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries (D-N.Y.) said in a joint letter to the executive director at DC Health Link on March 8. The letter sought specifics from the health exchange on the breach, including details on the full scope of the attack and DC Health Link’s plans to notify affected individuals and offer credit monitoring services for them.
Despite the letter, details of the intrusion at DC Health Link are not yet available. The organization, governed by an executive board appointed by the DC mayor, did not immediately respond to a request for comment on the incident.
A report in BleepingComputer this week first identified the threat actor as the appropriately named IntelBroker, after the cybercriminals put the stolen data up for sale on March 6. According to the underground forum ad, the data set is available for “an undisclosed amount in Monero cryptocurrency.” Interested parties are asked to contact the sellers via a middleman for details.
This is not the first big heist for the group: A threat actor, using the same moniker in February, had claimed credit for a breach at Weee!, an Asian and Hispanic food delivery service. IntelBroker later leaked some 1.1 million unique email addresses and detailed information on over 11.3 million orders placed via the service.
Security vendor BitDefender, which covered the incident in its blog at the time, published an ad that IntelBroker placed on BreachedForums that showed the attacker boasting about obtaining full names, email addresses, phone number, and even order notes which included apartment and building access codes.
Meanwhile, Chris Strand, chief risk and compliance officer at Cybersixgill says his company has been tracking IntelBroker since 2022 and is about to release a report on the actor. “IntelBroker is a highly active Breached member with an 9/10 reputation score, who claimed in the past to be the developer of Endurance ransomware,” Strand says.
IntelBroker’s use of Breached to sell the health exchange PII, instead of a dedicated leak site or a Telegram channel, is consistent with the threat actor’s previous tactics. It suggests either a lack of resources or inexperience on the individual’s part, Strand says.
“In addition to IntelBroker’s presence on Breached, the threat actor has maintained a public GitHub repository titled Endurance-Wiper,” he tells Dark Reading.
In November, IntelBroker claimed that it used Endurance to steal data from high level US government agencies, Strand notes. The threat actor has in total made some 13 claims about breaching top US government agencies, likely to attract customers to a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) program. Other organizations that IntelBroker claims to have broken into include Volvo, cult footwear maker Dr. Martens, and an Indonesian subsidiary of The Body Shop.
“Our intelligence analysts have been tracking IntelBroker since 2022, and we have been collecting intel attributed to that threat actor since then, as well as associated threats that have been related or attributed to IntelBroker,” Strand says.
Justin Fier, senior vice president of red team operations at Darktrace, says the threat actor’s reason for putting the data up for sale appears to be purely financially motivated rather than political. And given the high profile of the victims, IntelBroker may find that the attention the breach is garnering will increase the value of the stolen data (or bring more heat than it would like).
The buyers might be another story. Given the availability of physical addresses and electronic contact information, the kinds of potential follow-on attacks are myriad, ranging from social engineering for identity theft or espionage, to physical targeting, meaning that interested parties could run the gamut in terms of motivation.
“The amount tells you a great deal about who they may be thinking of in terms of buyers,” he says. If all that the threat actor ends up asking is a couple of thousand dollars, they are likely to be a smaller criminal enterprise. But “you start talking millions, they are clearly then catering to nation-state buyers,” he says.
Fier assesses that the data that the threat actor stole on US House members as potentially posing a national security issue. “We shouldn’t only think external nation-states that might want to purchase this,” Fier says. “Who is to say that other political parties and/or activists couldn’t weaponize it?”
Previous posts on Cyber Attacks

InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services
Mar 06 2023
LayerX has published its annual browser security report in which the company highlights the most prominent browser security risks of 2022. The report includes predictions and recommendations for 2023 as well.
The report focuses on Enterprise environments, but several of its key takeaways apply to small business and home environments as well. The browser security threats of 2022 make up the largest part of the document, but users find predictions, recommendations and an interesting monthly overview of major security events in the report as well.
The nine major threats that LayerX identified in 2022 were the following ones:
Some of these are quite clear, others may require explanation. For phishing attacks, the researchers discovered that threat actors are hosting phishing URLs on legitimate SaaS platforms at an alarming rate. The rate of phishing attacks that use these legitimate platforms has increased by 1100% when compared to 2021, according to a Palo Alto Networks study.
LayerX conducted tests on how well browsers and network security tools protected against 1-day phishing sites. According to the test, the best performing browser had a catch rate of just 36%. Network security software blocked 48% of threats.
Similarly, malware is distributed via sanctioned services such as Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive, to overcome blocks that may be in place for lesser known services and sites.
An analysis of data leakage in browsers concluded that 29% of users connected work browsers to personal profiles, and that 5.8% of identities were exposed in data breaches.
Outdated browsers are another threat to security, according to LayerX’s report. Ana analysis of 500 Chrome browsers revealed that a good number was either critically outdated or vulnerable to 1-day attacks.
Weak passwords and the reuse of passwords continue to be major issues. According to LayerX’s report, 29% of users use weak or medium strength passwords, and 11% of users reuse passwords regularly. The company noticed that 29% browser profiles were personal and set to sync.
Web browser extensions are another attack vector, as they “can grant excessive permissions once installed”. A recent Incogni study found that almost half of the analysed browser extensions posted either a high security or privacy risk.
The report includes an overview of browser security highlights of the year 2022. It is an interesting account that lists major security events in 2022. Some of these involved attacks, like the January 2022 video player attack that stole credit card information from over a hundred sites. Others highlight security advances, like the passwordless logins announcement by major tech companies in May, or the end of Internet Explorer in June.
The report ends with four predictions and recommendations. Predictions include that browsers will become “the main attack surface”, that attacks will “be increasingly SaaS-based and less file-based”, and that malicious web pages “will become more sophisticated”.
Closing Words
The report offers insights on the browser threat landscape of 2022, and how threats will evolve in 2023 and beyond. While most of it is aimed at Enterprise and large business environments, it may still be of interest to home users and small businesses alike.
The recommendations focus on SaaS and Enterprise-grade protections, but all users may use the listed threats to improve security. For example, outdated browsers may be updated more frequently, and weak or reused passwords may be replaced with unique strong passwords.
The report is available for download here, but a short form needs to be filled out before the download link is made available.
Source:
Previous posts on Web Security
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services
Web App Security

Feb 25 2023


Ethical Hacking Essentials (EHE)
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services
Feb 24 2023

Here are the top 10 infoSec blogs: by ChatGPT
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services
Feb 16 2023
A large number of e-commerce payment platforms use effective payment gateway tools and effectively integrate them with an acceptable payment strategy. Today’s e-commerce websites need to integrate anti-fraud tools, renew bank cards, integrate multiple gateways, and manage alternative payment methods.
It is important to get these complex integrations right and bring them together into one functioning system; choosing the right tokenization partner is the key to success in these processes.
Tokenization is an important process of replacing sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, with unique identifying information while preserving all important data information; a tokenization solution is a form of using a unique security key to provide an appropriate level of security to important confidential data.
Think of tokenization as a secret code that uses a key to retrieve an encrypted message. Some versions of the credit card number store the last four digits; however, the remaining digits of the credit number are random.
In this case, you can safely store the token in the database. Anyone with access to this token cannot use it to compromise your credit card account. For these tokens to be used to process credit card transactions, they must be re-linked to the original credit card numbers. Typically, this mapping is performed by a secure third party. All this is done to ensure full security.
Blockchain technology is a technology that most people associate only with cryptocurrencies. This attribution is not entirely incorrect, as the blockchain was created for the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. However, much has changed since 2009 (the year Bitcoin appeared), and the scope of blockchain technology continues to actively expand.
One of the key applications of this technology today is tokenization, a secure form of digitization based on the blockchain technology mentioned above. The process of tokenization consists of assigning a specific value to a symbol, which can exist materially or immaterially, and is a digital “token” that stores data. With this efficient solution, you can securely buy and sell your assets online.
Examples of this use of tokens include the value of the stock market. Most of us associate stocks and bonds with paper-based notices of ownership of those assets, but tokenization allows us to replace those paper notices with digital versions. The implementation of traditional solutions in the digital world simplifies and optimizes a large number of important processes, making them significantly more efficient.
The terms “token” and “cryptocurrency” are often confused and used interchangeably; not surprisingly, both concepts are closely related to blockchain technology. The key difference between cryptocurrencies and tokens is that cryptocurrencies are a means of payment, whereas tokens cannot; they can be compared to a kind of chip.
A token is created using smart contracts on a specific blockchain network and can perform various key functions. Each blockchain network can contain an unlimited number of tokens.
On the other hand, a smart contract is a kind of computer program embedded in a certain blockchain network that automatically enforces the terms contained in it. Both tokens and cryptocurrencies can be transferred on the blockchain network; however, token transaction fees depend on the cryptocurrency.
Tokenization is commonly used to protect credit card numbers, a process mandated by the Payment Card Industry Council (PCI). However, there are many different use cases, tokenization terminology allows you to learn a variety of effective tools that provide active growth in the field of security for business organizations for which it is important to reliably protect confidential data.
Consider personal or personally identifiable information. HIPPA, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires confidential processing, anonymization, and secure storage of personal data. Organizations and various business environments should use tokenization capabilities when the business needs to securely store confidential information, such as:
Due to the universality of tokens, they are divided into several types that perform different functions. One of the key differences is between mutual tokens and non-splitting tokens. For example, payment tokens are used to make payments. Their function is mainly to ensure the safety of investors. Issued security tokens are protected by law and represent specific stocks, bonds, or other assets of genuine interest.
Undoubtedly, there are many advantages to using tokens, but is it safe to store data? Security is considered one of the most important benefits of tokenization. Stability, irreversibility of transactions, and elimination of intermediaries are just some of the characteristics that affect security when using blockchain technology.
In addition, the security of tokenization is provided by smart contracts that allow parties to trade directly. For example, selling real estate in the form of tokens does not require a notary or a real estate agent. Everything is done quickly and directly.
Note that each contracting party must ensure that personal tokens are properly stored and protected from loss to properly act as guarantors of successful transactions. Tokenization is a form of business digitization based on blockchain technology.
The potential of tokenization is huge and has yet to be fully explored. Tokens are divided into different types. The most common use of tokens is to digitize different types of assets, such as physical assets, digital assets, projects, company shares, shares, or loans.
When it comes to PCI tokens, there are three key types of tokenization: gateway tokenization, end-to-end tokenization, and payment service tokenization. Gateway tokenization. When you do e-commerce, you most likely get paid through a payment gateway.
Most gateways have technology that allows you to securely store your credit card in the system, then issue a refund and delete your card data. The downside is that each gateway provides its token scheme. This means that you cannot use this gateway. Changing gateways is often a time-consuming and expensive process of moving customer data to a new gateway for secure processing.
In some cases, the gateway may not allow these actions. End-to-end tokenization. Some independent tokenization providers have their technology that sits between your e-commerce site and the gateway. These end-to-end token providers allow you to use your existing gateway integration code.
One of the key advantages of this type of tokenization is that it uses existing technology and can be adapted at a very fast pace. It also has the advantage of modularity. Unlike gateway tokenization, modularity can be actively used for more than just credit card payments. You can use the tokenization model to connect to most APIs and tokenize data other than credit card data.
End-to-end tokenization is an evolution of gateway tokenization. This gives payment solutions the freedom to route transactions to different gateways in real-time, avoiding costly and time-consuming transfers of card data between different payment platforms.
A key tokenization strategy is the payment service model. This model offers a single API that, when integrated, can route payments to multiple gateways. The payment service model is best suited for companies with more complex payment needs.
This model works well when a company needs to pay in several regions or several different currencies or through several gateways. A disadvantage of the payment service model is that existing gateway embed code cannot be reused.
In addition to reduced PCI coverage and increased security, the tokenized payment service model has unique key benefits from its active use. The payment services model not only simplifies your embed code but also takes control of your tokens away from the payment gateway. Unlike gateway tokenization, tokens provided by third parties can be actively used with supported gateways.
Tokens issued by payment gateways cannot be used against competing alternative gateways. Security and compliance alone are reasons enough to implement a popular solution like the tokenization of various assets that are important to you, your company, and your customers.
The truth is that key security requirements for online payments are difficult to implement on your own. In particular, startups often choose to sacrifice security for time to market. Accepting online payments makes your business a target for cybercriminals. Hiring security experts and implementing effective tokenization processes can save your business environment valuable time and money in the long run.
Keep these practical tips in mind. Choose a reliable tokenization partner, test the tokenization, what level of protection you can achieve by working on the integration, and find a vendor that can integrate multiple gateways, methods, and services into a single integration. One of the key technologies needed to connect all payment solutions is tokenization.
A trusted provider fully controls tokens, provides redundancy, reduces PCI coverage, and improves the security standards in place in your business environment.
The use cases for tokenization can grow endlessly. Since anything can be digitized, tokenization is often used in professional life. These are various business projects that can demonstrate the most practical examples of using tokenization.
Digitization of the company involves the creation of tokens that are closely related to a specific project. Tokenization techniques that add value to tokens can be used as an indispensable tool for automating processes in companies and as a means of financing them. Real estate tokenization is becoming more and more popular worldwide due to the following features: transaction speed, lack of intermediaries, and security.
The process of property tokenization involves issuing tokens on the blockchain network and linking them to certain properties. Thus, the investor becomes a co-owner or owner of a certain asset, the shares of which can be represented in tokens.
Using blockchain technology and a specially designed platform, it is also possible to assign unique numbers to gems and certain forms of ore to determine their authenticity.
Raw materials registered with digital numbers can then be identified by verifying their origin, properties, and associated processes. NFT tokens have the unique potential to revolutionize both the physical and digital art markets. Each NFT token has a unique, non-tradable value that allows you to express your interest in the rights to a work of art, making investing in art an easy and fast process.

Digital Finance: Security Tokens and Unlocking the Real Potential of Blockchain
Blockchain and the Future of Finance
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services
Feb 12 2023
Feb 10 2023
Welcome to our February 2023 review of phishing attacks, in which we explore the latest email scams and the tactics that cyber criminals use to trick people into handing over personal data.
This month, we look at a UK government warning about a resurgence in Russian cyber attacks and concerns that the much-discussed AI programme ChatGPT could be used for fraud.
The UK government has issued a warning amid an increase in phishing attacks stemming from Russia and Iran.
In an advisory statement, the NCSC (National Cyber Security Centre) shared details about the campaign, which appears to have been sponsored by the fraudsters’ national governments.
The researchers are most concerned about spear phishing, which is a sophisticated form of fraud. Scammers target specific individuals by researching them online – often using Facebook, LinkedIn or the website of the target’s employer.
Although spear phishing emails often contain the same clues as regular phishing scams, they have a much higher success rate. This suggests that people are more likely to assume that a message is genuine if it contains a few specific details about them, such as their name or their place of work.
The NCSC’s advisory highlights ongoing scams that were conducted throughout last year by the Russia-based group SEABORGIUM and the Iran-based group TA453, also known at APT42.
Their attacks target specific sectors within the UK, including academia, defence, governmental organisations, NGOs and thinktanks, as well as politicians, journalists and activists.
Commenting on the findings, NCSC Director of Operations Paul Chichester said: “The UK is committed to exposing malicious cyber activity alongside our industry partners and this advisory raises awareness of the persistent threat posed by spear-phishing attacks.
“These campaigns by threat actors based in Russia and Iran continue to ruthlessly pursue their targets in an attempt to steal online credentials and compromise potentially sensitive systems.
“We strongly encourage organisations and individuals to remain vigilant to potential approaches and follow the mitigation advice in the advisory to protect themselves online.”

ChatGPT has taken the Internet by storm, with the AI-backed tool helping writers and hobbyists create content almost instantly.
The program’s advanced language model has been championed by people looking to quickly produce quotes, articles and think pieces. However, cyber security experts are warning that another group – scammers – could also embrace the technology.
As Chester Wisniewski, the principal research scientist as Sophos, explained, ChatGPT can instantly produce grammatically correct and natural-looking writing, which would resolve one the biggest challenges that scammers face when creating their baits.
“The first thing I do whenever you give me something is figuring out how to break it. As soon as I saw the latest ChatGPT release, I was like, ‘OK, how can I use this for bad things?’ I’m going to play to see what bad things I can do with it,” Wisnieski told TechTarget.
One of those ‘bad things’ that he considered was the ability for ChatGPT to create phishing scams.
“If you start looking at ChatGPT and start asking it to write these kinds of emails, it’s significantly better at writing phishing lures than real humans are, or at least the humans who are writing them,” he said.
“Most humans who are writing phishing attacks don’t have a high level of English skills, and so because of that, they’re not as successful at compromising people.
“My concerns are really how the social aspect of ChatGPT could be leveraged by people who are attacking us. The one way we’re detecting them right now is we can tell that they’re not a professional business.
“ChatGPT makes it very easy for them to impersonate a legitimate business without even having any of the language skills or other things necessary to write a well-crafted attack.”
All organisations are vulnerable to phishing, no matter their size or sector, so it’s essential to understand how you might be targeted and what you can do to prevent a breach.

You can help educate your staff with IT Governance’s Phishing Staff Awareness Training Programme.
This 45-minute course uses real-world examples like the ones we’ve discussed here to explain how phishing attacks work, the tactics that cyber criminals use and how you can detect malicious emails.
More resources on Phishing training
InfoSec Threats | InfoSec books | InfoSec tools | InfoSec services

Feb 08 2023
Jan 31 2023