De-perimeterization term has been around almost for a decade and finally industry is taking it seriously because of virtualization and cloud computing popularity. Is it time for businesses to emabrace de-perimeterization?
De-perimeterization is a double edge sword for industry which creates scalable options for operation and huge challenges for safeguarding the assets beyond the edge. One of the major advantages for de-perimeterization is that user can access corporate information over the internet; in this situation user can access corporate data from any where, it’s hard to draw the line where the edge begins and where it ends. All you basically need a functional laptop with internet connection. On the other hand, de- perimeterization poses a great challenge due to possibility of viruses, spywares and worms spreading in your internal protected infrastructure.
In de-perimeterized environment, security attributes shall follow the data, wherever the data may go or reside.
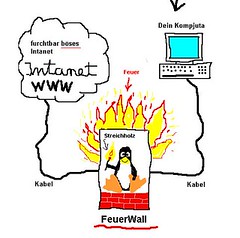
In security architecture where firewall was considered a very effective perimeter defense has been weakens by virtualization and cloud computing. In early days of firewall defense, organization only needed to open few necessary protocols and ports to do business. Internet accessible systems were located on the DMZ and the communication was initiated from the corporate to internet. Now there are whole slew of protocols and ports which needs to be open to communicate with application in the cloud. As corporate application move out of the organization network into the cloud, the effectiveness of firewall diminished.
Defense in depth is required for additional protection of data because as new threats emerge, the firewall cannot be used as an only layer of security. The key to the security of de-perimeterization is to push security at each layer of infrastructure including application and data. Data is protected at every layer to ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA). Various techniques can be utilized for safeguarding data including data level authentication. The idea of data level authentication is that data is encrypted with specific privileges, when the data move, those privileges are moved with the data.

Endpoint security is relevant in today’s business environment especially for laptop and mobile devices. Agents on laptops and mobile devices utilized pull/push techniques to enforce relevant security policies. Different policies are applied depending on the location of the laptop. Where security policy will ensure which resources are available and what data need to be encrypted depending on the location of the device.
When corporate application and important data reside in the cloud, SLA should be written to protect the availability of the application and confidentiality of the data. Organizations should do their own business continuity planning so they are not totally dependent on the cloud service provider. For example backup your important data or utilize remote backup services where all data stored is encrypted.
Cloud Security and Privacy: An Enterprise Perspective on Risks and Compliance
Download a free guide for following cloud computing applications
Hosted email solution
Hosted email archiving
Hosted web monitoring
Hosted online backup
Tags: business continuity, Cloud computing, cloud computing article, cloud computing concerns, cloud computing email, cloud computing hosting, cloud computing information, cloud computing security, cloud computing services, cloud security, cloud services, de-perimeterizations, DMZ, iso assessment





![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](https://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=3a8e0883-feb2-4865-b29d-67dedeb875d5)
 Cloud computing is the future of the computing, which happens to provide common business applications online that run from web browser and is comprised of virtual servers located over the internet. Basic idea behind cloud computing is the accessibility of application and data from any location as long as you are connected to the internet. Cloud computing makes the
Cloud computing is the future of the computing, which happens to provide common business applications online that run from web browser and is comprised of virtual servers located over the internet. Basic idea behind cloud computing is the accessibility of application and data from any location as long as you are connected to the internet. Cloud computing makes the![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](https://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=e7f7ca92-d521-4be7-b5c4-dfc3282c607f)


