Apache HTTP Server is one of the web servers that is used the most often throughout the globe. It is responsible for providing power to millions of websites and apps. Recent vulnerabilities found in the server, on the other hand, have the ability to disclose sensitive information and make it easier for attackers to carry out further attacks. The Apache HTTP Server has recently been found to contain two significant vulnerabilities, both of which are detailed below. It is imperative that you rapidly upgrade Apache HTTP Server to the most recent version in order to protect your system against the vulnerabilities described.

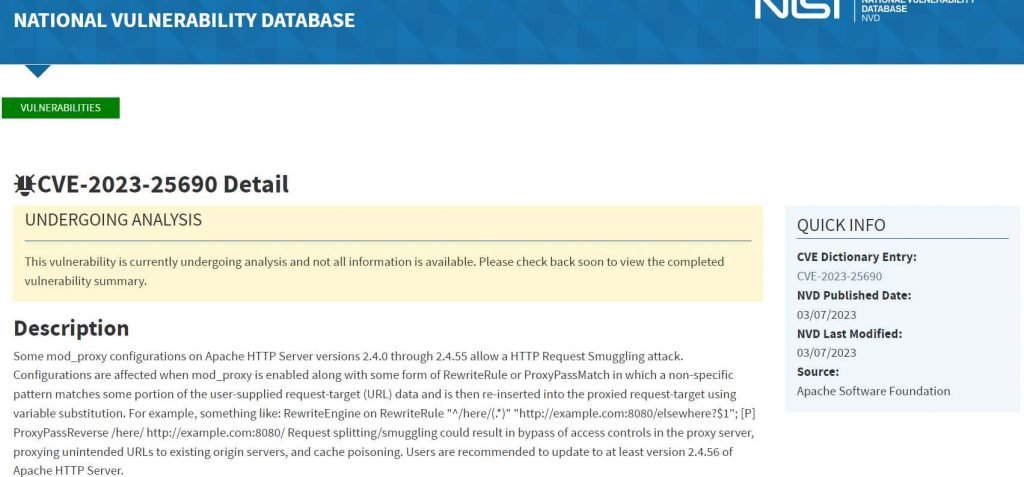
Apache HTTP Server request splitting vulnerability, CVE-2023-25690. This vulnerability is brought about by an issue that occurs in mod proxy whenever it is activated with a RewriteRule or ProxyPassMatch of some kind. This vulnerability might be used by a remote attacker to overcome access constraints in the proxy server, route undesired URLs to existing origin servers, and poison cache. Attacks using HTTP Request Smuggling are possible on Apache HTTP Server versions 2.4.0 through 2.4.55, if the server is configured with certain mod proxy settings. It occurs when mod proxy is enabled along with some form of RewriteRule or ProxyPassMatch. In these configurations, a non-specific pattern matches some portion of the user-supplied request-target (URL) data, and the matched data is then re-inserted into the proxied request-target utilizing variable substitution. This causes CVE-2023-25690 to be triggered. This might result in requests being split or smuggled, access rules being bypassed, and unwanted URLs being proxied to existing origin servers, all of which could lead to cache poisoning.
Versions of the Apache HTTP Server ranging from 2.4.30 to 2.4.55 are impacted by the problem. This attack is carried out by introducing unusual characters into the header of the origin response, which has the potential to either truncate or divide the response that is sent to the client. An attacker might take use of this vulnerability to inject their own headers into the request, causing the server to produce a split response.



![INSTRUCTIONS FOR SET UP SECURITY POLICY WEB SERVER APACHE by [David Du]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/41uFA2ri8YL.jpg)


